Available Questions Page 1 of 14
Standalone Questions
#985
Physics
Nuclei
VSA
APPLY
2025
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
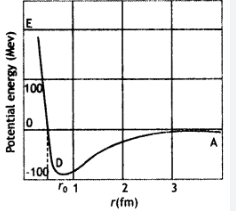 State two important properties of the nuclear force.
State two important properties of the nuclear force.
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
hkdcdj ds
#982
Physics
Alternating Current
#969
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
MCQ_SINGLE
UNDERSTAND
2025
AISSCE(Board Exam)
KNOWLEDGE
1 Marks
(A) $y = \sin^{-1} x$ and $y = \cos^{-1} x$
(B) $y = \cos^{-1} x$ and $y = \cos x$
(C) $y = \sin^{-1} x$ and $y = \sin x$
(D) $y = \cos^{-1} x$ and $y = \sin x$
Key: C
Sol:
Sol:
#968
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
MCQ_SINGLE
REMEMBER
2025
AISSCE(Board Exam)
KNOWLEDGE
1 Marks
(A) $y = \tan^{-1}x$
(B) $y = \csc^{-1}x$
(C) $y = \cot^{-1}x$
(D) $y = \sec^{-1}x$
Key: A
Sol:
Sol:
#945
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2024
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Express \(\tan^{-1}(\frac{\cos~x}{1-\sin~x})\) where \(\frac{-\pi}{2}\lt x\lt \frac{\pi}{2}\) in the simplest form.
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
Let $y = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{\cos x}{1-\sin x}\right)$.First, use half-angle identities to rewrite the numerator and denominator:$$\cos x = \cos^2\frac{x}{2} - \sin^2\frac{x}{2} = \left(\cos\frac{x}{2} - \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)\left(\cos\frac{x}{2} + \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)$$$$1 - \sin x = \cos^2\frac{x}{2} + \sin^2\frac{x}{2} - 2\sin\frac{x}{2}\cos\frac{x}{2} = \left(\cos\frac{x}{2} - \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)^2$$Substitute these back into the expression:$$\frac{\cos x}{1-\sin x} = \frac{\left(\cos\frac{x}{2} - \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)\left(\cos\frac{x}{2} + \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)}{\left(\cos\frac{x}{2} - \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)^2}$$Cancel the common term $\left(\cos\frac{x}{2} - \sin\frac{x}{2}\right)$:$$= \frac{\cos\frac{x}{2} + \sin\frac{x}{2}}{\cos\frac{x}{2} - \sin\frac{x}{2}}$$Divide the numerator and denominator by $\cos\frac{x}{2}$:$$= \frac{1 + \tan\frac{x}{2}}{1 - \tan\frac{x}{2}}$$Since $\tan\frac{\pi}{4} = 1$, we can rewrite this as:$$= \frac{\tan\frac{\pi}{4} + \tan\frac{x}{2}}{1 - \tan\frac{\pi}{4}\tan\frac{x}{2}}$$Using the identity $\tan(A+B) = \frac{\tan A + \tan B}{1 - \tan A \tan B}$:$$= \tan\left(\frac{\pi}{4} + \frac{x}{2}\right)$$Therefore:$$y = \tan^{-1}\left(\tan\left(\frac{\pi}{4} + \frac{x}{2}\right)\right)$$Since $x \in (-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2})$, the angle lies within the principal range, so:$$y = \frac{\pi}{4} + \frac{x}{2}$$
#944
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2024
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Find the value of \(\tan^{-1}(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}})+\cot^{-1}(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}})+\tan^{-1}[\sin(-\frac{\pi}{2})].\)
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
Let the given expression be $E$.$$E = \tan^{-1}\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right) + \cot^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right) + \tan^{-1}\left[\sin\left(-\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\right]$$Evaluate each term separately using principal values:$\tan^{-1}\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right) = -\frac{\pi}{6}$(Since $\tan\frac{\pi}{6} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ and $\tan^{-1}(-x) = -\tan^{-1}x$)$\cot^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right) = \frac{\pi}{3}$(Since $\cot\frac{\pi}{3} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$)For the third term, first evaluate the sine function:$\sin\left(-\frac{\pi}{2}\right) = -1$So, $\tan^{-1}(-1) = -\frac{\pi}{4}$Substitute these values back into the expression:$$E = -\frac{\pi}{6} + \frac{\pi}{3} - \frac{\pi}{4}$$Find a common denominator (which is 12):$$E = \frac{-2\pi + 4\pi - 3\pi}{12}$$$$E = \frac{-\pi}{12}$$
#943
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2024
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Find the domain of the function \(f(x)=\sin^{-1}(x^{2}-4).\) Also, find its range.
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
Domain
We need the argument of the arcsine to be in $[-1, 1]$:$$-1 \le x^2 - 4 \le 1$$Add 4 to all parts:$$3 \le x^2 \le 5$$Taking the square root, we get two intervals:$$\sqrt{3} \le |x| \le \sqrt{5}$$This splits into positive and negative regions:$$x \in [-\sqrt{5}, -\sqrt{3}] \cup [\sqrt{3}, \sqrt{5}]$$
Range
From the inequality above, we know that as $x$ varies over the domain, the term $(x^2 - 4)$ covers the entire interval $[-1, 1]$.Therefore, $f(x)$ covers all possible values of $\sin^{-1}(u)$:$$y \in \left[-\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2}\right]$$
#942
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2024
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Find the principal value of \(\tan^{-1}(1)+\cos^{-1}(-\frac{1}{2})+\sin^{-1}(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}).\)
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
Let the expression be $E$.$$E = \tan^{-1}(1) + \cos^{-1}\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right) + \sin^{-1}\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)$$
Evaluate each term using principal value branches:
$\tan^{-1}(1) = \frac{\pi}{4}$(Since $\tan\frac{\pi}{4} = 1$)
$\cos^{-1}\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right) = \pi - \frac{\pi}{3} = \frac{2\pi}{3}$(Since $\cos^{-1}(-x) = \pi - \cos^{-1}x$)
$\sin^{-1}\left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right) = -\frac{\pi}{4}$(Since $\sin^{-1}(-x) = -\sin^{-1}x$)
Substitute these values back into $E$:$$E = \frac{\pi}{4} + \frac{2\pi}{3} - \frac{\pi}{4}$$Cancel the $\frac{\pi}{4}$ terms:$$E = \frac{2\pi}{3}$$
#941
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2024
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Evaluate: \(\sec^{2}(\tan^{-1}\frac{1}{2})+cosec^{2}(\cot^{-1}\frac{1}{3})\)
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#939
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2025
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Simplify \(\sin^{-1}(\frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}).\)
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#938
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
#937
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2025
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Find the domain of the function \(f(x)=\cos^{-1}(x^{2}-4).\)
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#936
Mathematics
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
VSA
APPLY
2025
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Find the domain of \(f(x)=\sin^{-1}(-x^{2})\).
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#931
Mathematics
Applications of Derivatives
VSA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
Find the maximum and minimum values of the function given by \(f(x)=5+\sin 2x\).
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#927
Mathematics
Linear Programming
SA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
3 Marks
30. Solve the following linear programming problem graphically: Minimise: $z=-3x+4y$ subject to the constraints $x+2y\le8, 3x+2y\le12, x,y\ge0$
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#926
Mathematics
Vector Algebra
VSA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
If $\vec{r}=3\hat{i}-2\hat{j}+6\hat{k}$, find the value of $(\vec{r}\times\hat{j})\cdot(\vec{r}\times\hat{k})-12$
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#925
Mathematics
Vector Algebra
VSA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
2 Marks
24. If the projection of the vector $\hat{i}+\hat{j}+\hat{k}$ on the vector $p\hat{i}+\hat{j}-2\hat{k}$ is $\frac{1}{3}$, then find the value(s) of $p$.
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#924
Mathematics
Matrices and Determinants
LA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
5 Marks
If $A=\begin{bmatrix}1&2&-2\\ -1&3&0\\ 0&-2&1\end{bmatrix}$ and $B^{-1}=\begin{bmatrix}3&-1&1\\ -15&6&-5\\ 5&-2&2\end{bmatrix},$ find $(AB)^{-1}$.
OR Solve the following system of equations by matrix method :$ x+2y+3z=6, 2x-y+z=2, 3x+2y-2z=3.$
OR Solve the following system of equations by matrix method :$ x+2y+3z=6, 2x-y+z=2, 3x+2y-2z=3.$
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#919
Mathematics
Differential Equations
SA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
3 Marks
Solve the following differential equation : $xe^{\frac{y}{x}}-y+x\frac{dy}{dx}=0$
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
#918
Mathematics
Differential Equations
SA
APPLY
2023
KNOWLEDGE
3 Marks
Find the general solution of the differential equation : $\frac{d}{dx}(xy^{2})=2y(1+x^{2})$
Key:
Sol:
Sol:
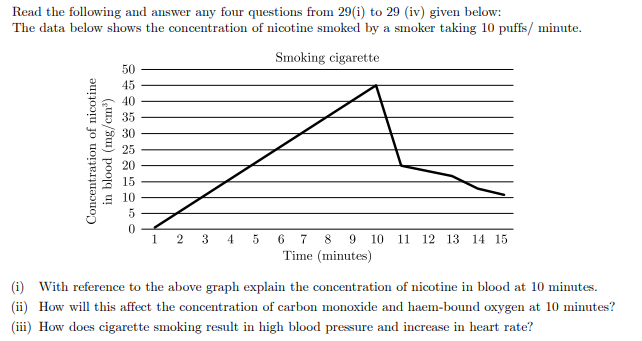 graph plot and analyze
graph plot and analyze